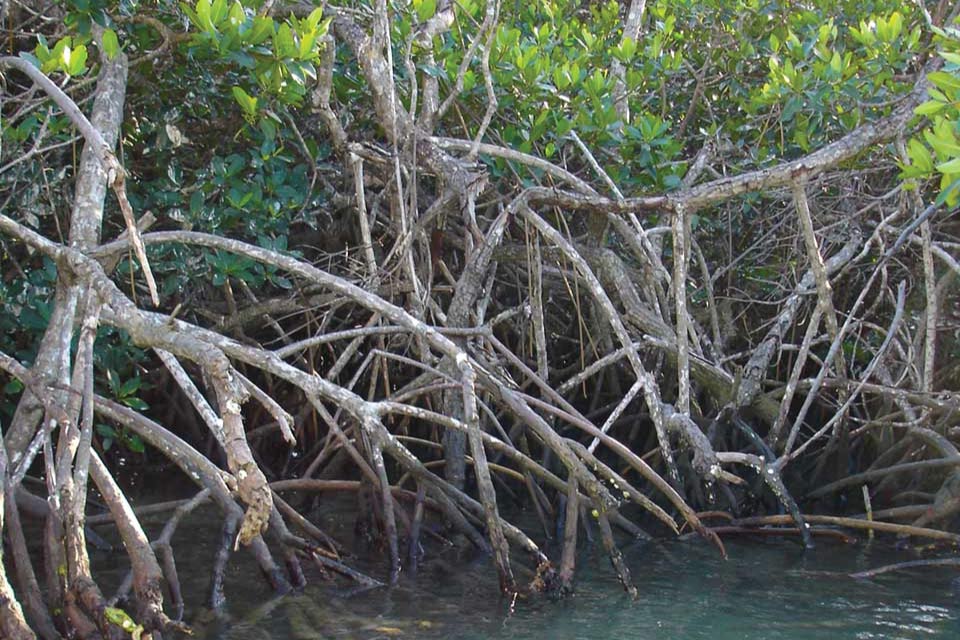
Sure, that is a picture of a mangrove, however do you know additionally it is a picture of a sink? A carbon sink. Don’t know what that’s? Learn beneath.
Do you know?
NOAA’s Nationwide Estuarine Analysis Reserves and their companions are working to make wetlands conservation and restoration worthwhile whereas lessening greenhouse fuel emissions via blue carbon monetary markets. These markets steadiness tasks that function heat-trapping emissions with contributions that take carbon out of the environment. Efforts so far have produced the first-ever U.S. information that makes salt marsh restoration eligible for worldwide carbon markets; analysis that paperwork carbon storage capabilities within the marsh; workshops and faculty curricula on the subject; and newsletters and technical help.
One thing that has a big impact on our day by day lives and is saved throughout the largest system of water on our planet should be a family identify, proper? Not essentially. Have you ever ever heard of blue carbon? Chances are high the reply isn’t any, however maybe you understand greater than you understand.
Blue carbon is just the time period for carbon captured by the world’s ocean and coastal ecosystems. You have got in all probability heard that human actions emit (or give off) one thing known as carbon dioxide, which comprises atmospheric carbon. You have got additionally heard that these gases are altering the world’s local weather, and never in a great way. What you might not have heard is that our ocean and coasts present a pure method of lowering the affect of greenhouse gases on our environment, via sequestration (or taking in) of this carbon.
Sea grasses, mangroves, and salt marshes alongside our coast “seize and maintain” carbon, performing as one thing known as a carbon sink. These coastal programs, although a lot smaller in measurement than the planet’s forests, sequester this carbon at a a lot sooner price, and might proceed to take action for hundreds of thousands of years. A lot of the carbon taken up by these ecosystems is saved beneath floor the place we will not see it, however it’s nonetheless there. The carbon present in coastal soil is usually 1000’s of years outdated!
The larger image of blue carbon is one in every of coastal habitat conservation. When these programs are broken, an infinite quantity of carbon is emitted again into the environment, the place it may well then contribute to local weather change. So defending and restoring coastal habitats is an effective option to scale back local weather change. Once we defend the carbon in coastal programs, we defend wholesome coastal environments that present many different advantages to individuals, comparable to leisure alternatives, storm safety, and nursery habitat for business and leisure fisheries.
One technique of slowing local weather change impacts is to include coastal wetlands into the carbon market via the shopping for and promoting of carbon offsets. This strategy creates a monetary incentive for restoration and conservation tasks by serving to to alleviate federal and state carbon taxes aimed toward discouraging the usage of fossil fuels. When fewer greenhouse gases are emitted, much less air pollution is created. When there’s much less air pollution to tax, the method advantages not solely the surroundings but additionally the monetary well-being of the group doing the restoration.