A tropical cyclone is a rotating low-pressure climate system that has organized thunderstorms however no fronts (a boundary separating two air lots of various densities). Tropical cyclones with most sustained floor winds of lower than 39 miles per hour (mph) are referred to as tropical depressions. These with most slot spadegaming rtp tertinggi winds of 39 mph or larger are referred to as tropical storms.
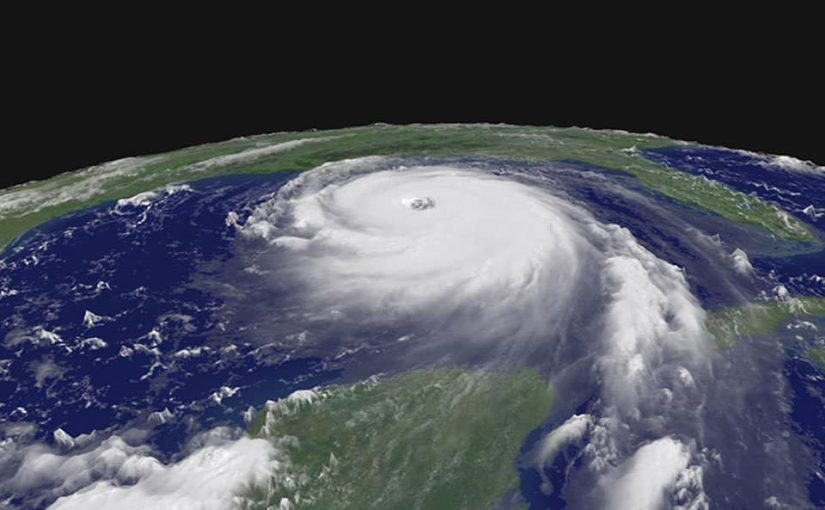
When a storm’s most sustained winds attain 74 mph, it’s referred to as a hurricane. The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a 1 to five score, or class, primarily based on a hurricane’s most sustained winds. The upper the class, the higher the hurricane’s potential for property injury.
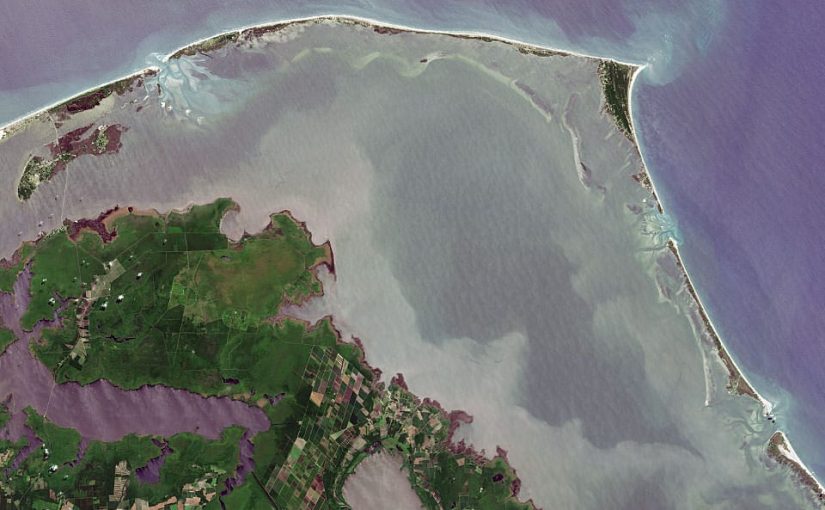
Hurricanes originate within the Atlantic basin, which incorporates the Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of Mexico, the jap North Pacific Ocean, and, much less often, the central North Pacific Ocean. A six-year rotating listing of names, up to date and maintained by the World Meteorological Group, is used to determine these storms.
“Hurricane Season” begins on June 1 and ends on November 30, though hurricanes can, and have, occurred outdoors of this timeframe. NOAA’s Nationwide Hurricane Middle predicts and tracks these large storm techniques, which happen, on common, 12 occasions a 12 months within the Atlantic basin.
As a world chief in hurricane analysis, NOAA strives to know the mechanics of those advanced storms to be able to defend individuals, property, commerce, and pure sources.
Video Transcript
When the utmost sustained winds of a tropical storm attain 74 miles per hour, it’s referred to as a hurricane. Hurricane Season begins on June 1 and ends on November 30, however these highly effective storms can happen earlier than and after the official season. A hurricane might be an superior and damaging drive of nature. Be ready. Go to Prepared.gov