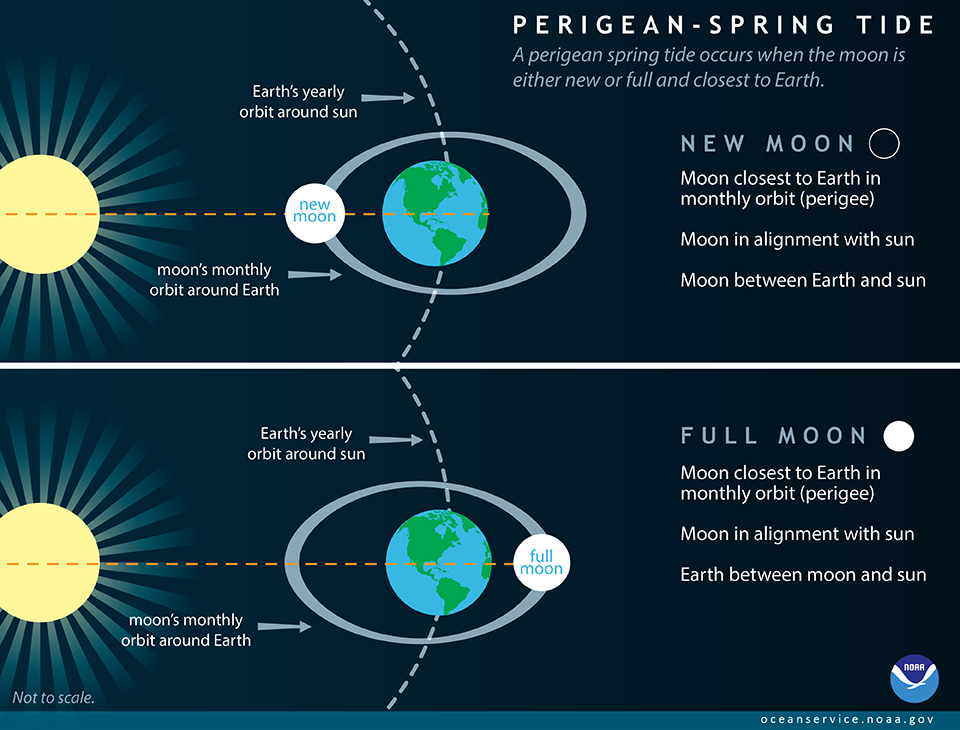
Typically between 6-8 occasions a 12 months, the brand new or full moon coincides intently in time with the perigee of the moon — the purpose when the moon is closest to the Earth. These occurrences are sometimes known as ‘perigean spring tides.’ Excessive tides throughout perigean spring tides will be considerably greater than throughout different occasions of the 12 months.
In an effort to perceive the phenomenon known as a ‘perigean spring tide,’ you first should know that the gravitational pull of the moon and the solar trigger tides. Tides are literally long-period waves that roll across the planet because the ocean is ‘pulled’ forwards and backwards because the moon and the solar work together with the Earth of their month-to-month and yearly orbits.
The following factor it is advisable to know is that the moon follows an elliptical path across the Earth in its month-to-month orbit, and the Earth follows an elliptical path in its yearly orbit across the solar. Which means that, at occasions, the moon and the solar are nearer to Earth. At different occasions, they’re farther away. What occurs when the moon and the solar are near the Earth? You guessed it: the gravitational pull they exert is stronger, leading to barely greater tides.
Whereas each the moon and the solar affect tides, the moon performs a a lot bigger position as a result of it’s so near the Earth. Its gravitational pull is about twice as sturdy as that of the solar. Now think about these two instances:
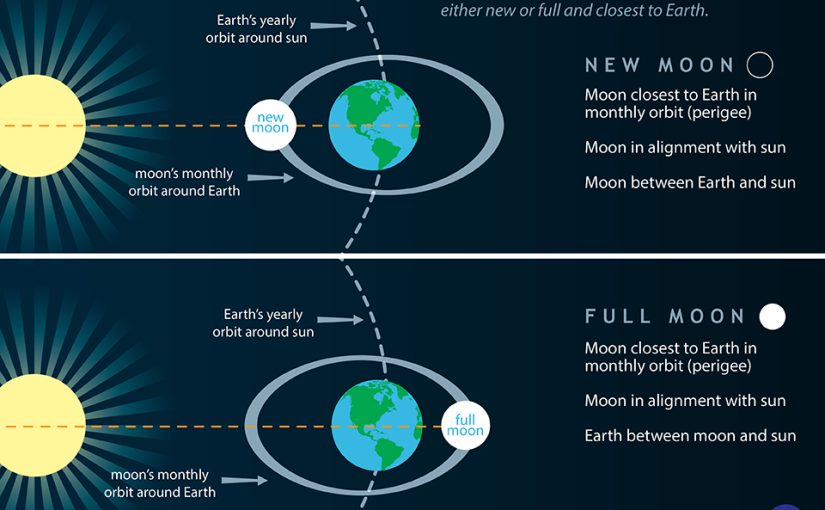
The Impact of a Full or New Moon
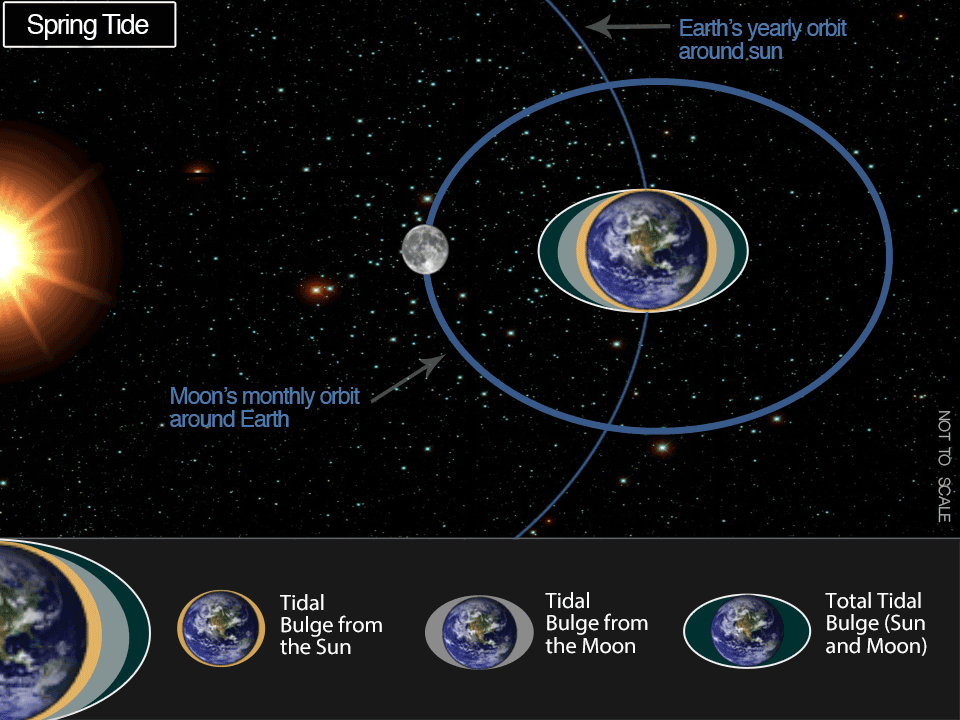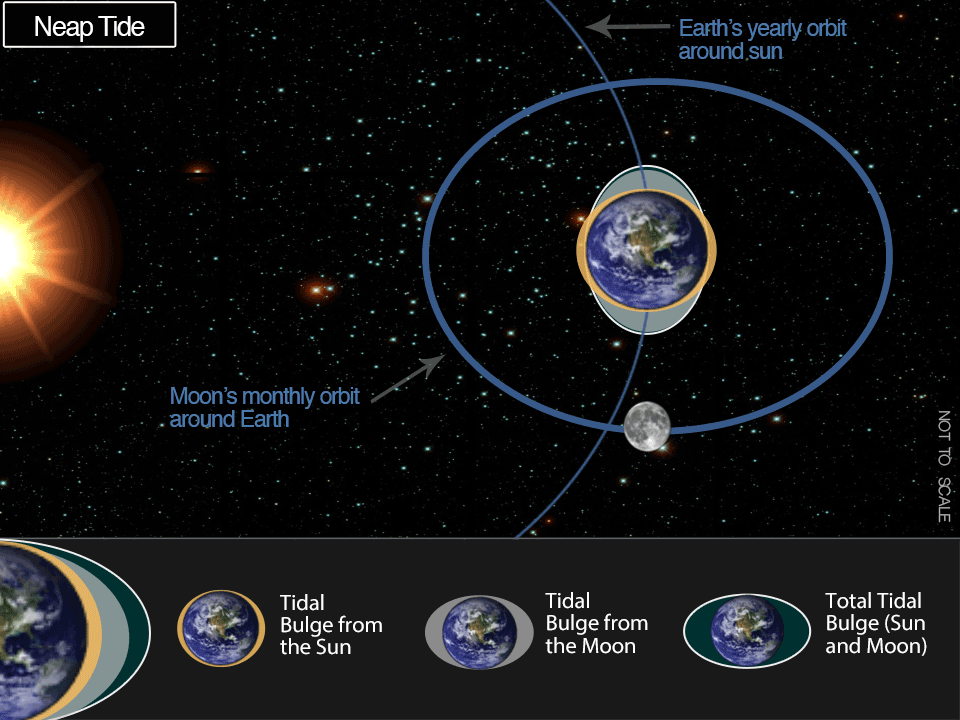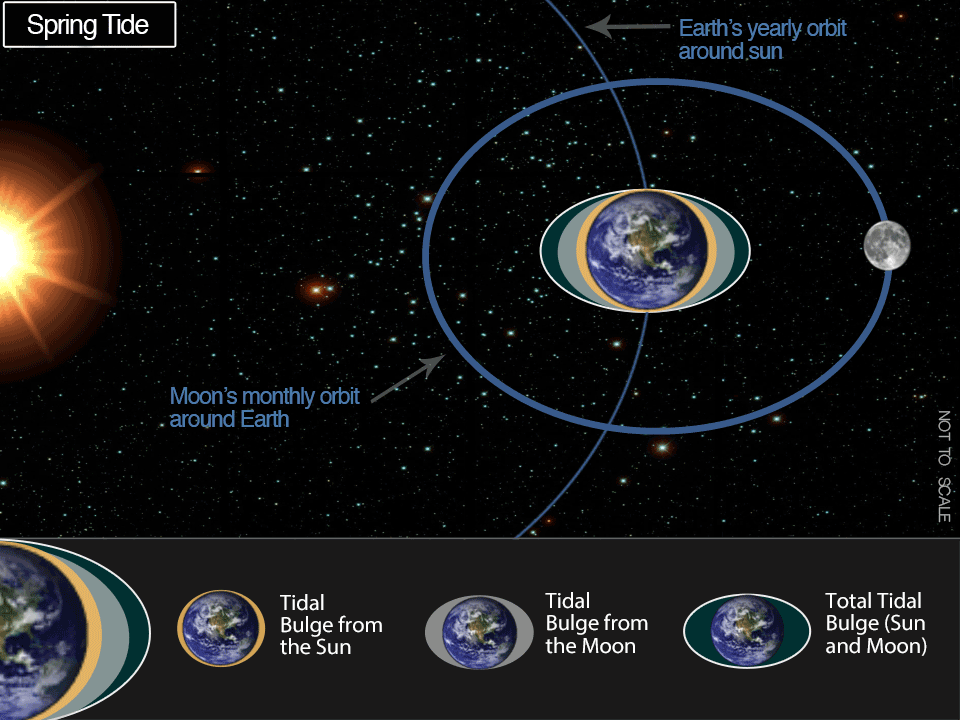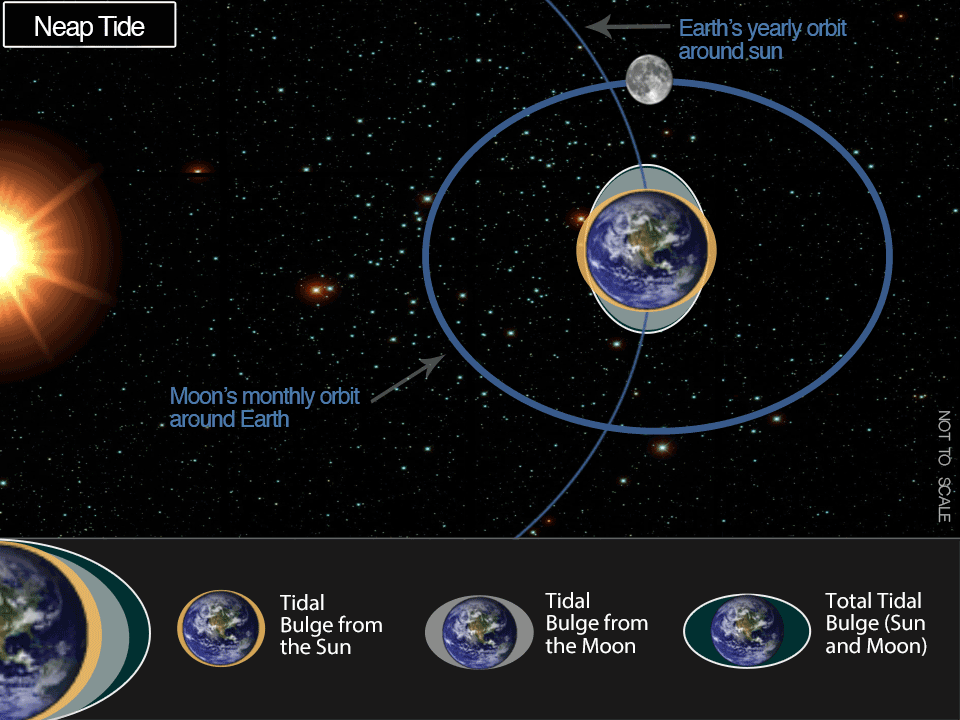
Throughout full or new moons — which happen when the Earth, solar, and moon are practically in alignment — common tidal ranges are barely bigger. This happens twice every lunar month (about 29.5 days on common). The moon seems new (darkish) when it’s between the Earth and the solar. The moon seems full when the Earth is between the moon and the solar. In each instances, the gravitational pull of the solar is ‘added’ to the gravitational pull of the moon on Earth, inflicting the oceans to bulge a bit greater than regular. Which means that excessive tides are greater and low tides are decrease than common. These are known as ‘spring tides.’

NOAA’s Excessive Tide Bulletin and Flooding Reviews
There are a lot of elements that trigger the tides to be greater than what’s “usually” seen from each day. Our seasonal bulletin tells you when it’s possible you’ll expertise greater than regular excessive tides the place you reside. We additionally publish annual excessive tide flooding stories that current a broad outlook of what to anticipate for a given 12 months when it comes to excessive tide flooding, in addition to a abstract of excessive tide flooding occasions for the earlier calendar 12 months.
The Impact of Perigee
As soon as about each 28 days, the moon reaches a ‘perigee,’ its closest level of strategy to the Earth. That is the purpose at which the gravitational pull of the moon is strongest. Throughout these durations there shall be a rise within the common vary of tides. Conversely, about 14 days following the perigee, the moon reaches an ‘apogee’, its furthest level of strategy to the Earth. That is the purpose at which the gravitation pull of the moon is weakest. Throughout these durations there shall be a lower within the common vary of tides.
What occurs when a full or new moon coincides with perigee?
Full or New Moon + Perigee
Sometimes between 6-8 occasions annually, the brand new or full moon coincides intently in time with the perigee of the moon — the purpose when the moon is closest to the Earth. These occurrences are sometimes known as ‘perigean spring tides.’ The distinction between perigean spring tides and spring tides that happen nearer to the moon’s apogee are location dependent and considerably influenced by tidal vary, however will be fairly massive. It isn’t unusual for top tides throughout a perigean spring tide to be greater than a foot greater than excessive tides throughout ‘apogean spring tides’. In locations like Anchorage, Alaska, which has a tidal vary over 30 ft, the distinction between spring tides will be 3 ft or extra at excessive tide!
It is also vital to notice that different elements affect the peak of the tide as effectively. Seasonal results on imply water degree and the tide, like greater water degree because of the thermal growth of hotter water, can generally imply that a number of the highest tides of the 12 months aren’t perigean spring tides.
Perigean Spring Tides and Coastal Flooding
Coastal flooding would not at all times happen each time there’s a perigean spring tide. Nevertheless, perigean spring tides mixed with seasonal adjustments within the tide and imply sea degree could trigger minor coastal flooding in some low-lying areas, sometimes called “excessive tide flooding” or “nuisance flooding”. Main coastal flooding sometimes happens in response to sturdy onshore winds and barometric strain adjustments from a coastal storm. If a storm strikes throughout a perigean spring tide, flooding could possibly be considerably worse than it in any other case would have been. In some cases, perigean spring tides have coincided with a shift in offshore ocean circulation patterns and enormous scale shifts in wind which have resulted in sudden coastal flooding. It’s anticipated that occurrences of minor excessive tide flooding on the occasions of perigean spring tides will improve much more as sea degree rises relative to the land. NOAA’s tide and tidal present predictions consider astronomical issues because of the place of the moon and the solar.