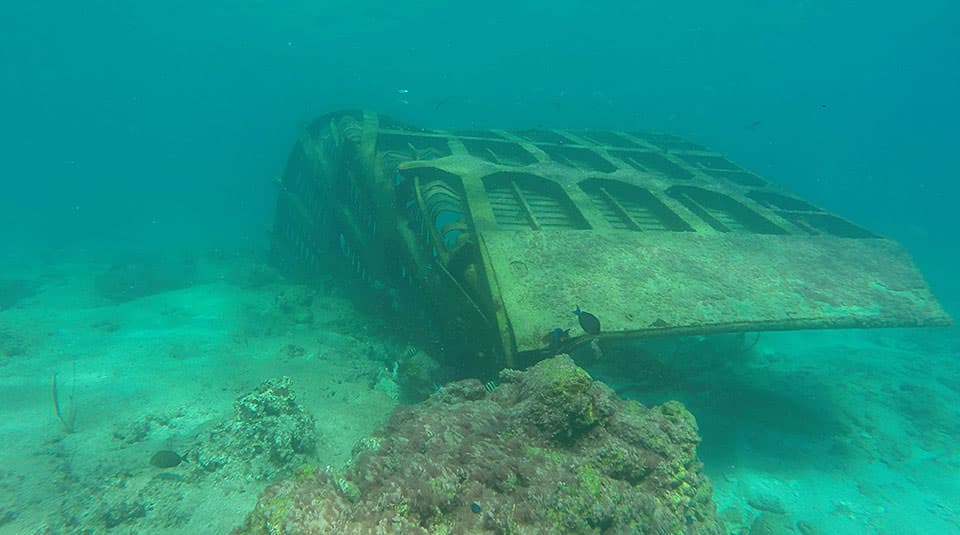
A sunken vessel amongst a coral colony in Vieques, Puerto Rico, on Oct. 23, 2017. Following Hurricane Maria in 2017, NOAA and companions eliminated a complete of 479 displaced vessels and three,668 hazardous chemical containers. Groups additionally relocated roughly 400 coral colonies.
When a storm churns throughout the ocean, the nice and cozy floor waters present further moisture and
can gasoline the storm right into a hurricane. Because the hurricane grows bigger and stronger, it may possibly
generate waves as excessive as 18.3 meters (60 ft), tossing and mixing hotter floor waters with the colder,
saltier water under. The ensuing currents can lengthen so far as 91.5 meters (300 ft) under the
floor, wreaking lethal havoc on marine life.
If the wild currents fail to interrupt up coral reefs of their path, the rain-infused water they bring about
reduces salt ranges and in any other case stresses corals. Because the hurricane strikes towards shore, the
underwater tumult could cause shifting sands and muddy shallow waters, blocking the important
daylight on which corals and different sea creatures rely.
Gradual-moving fish and turtles and shellfish beds are sometimes decimated by the tough undercurrents
and fast modifications in water temperature and salinity wrought by a hurricane. Sharks, whales, and
different massive animals swiftly transfer to calmer waters, nevertheless, and, usually talking, usually are not
overly affected by hurricanes.