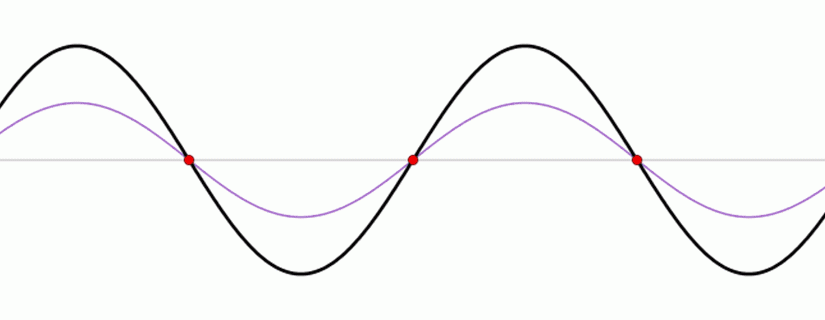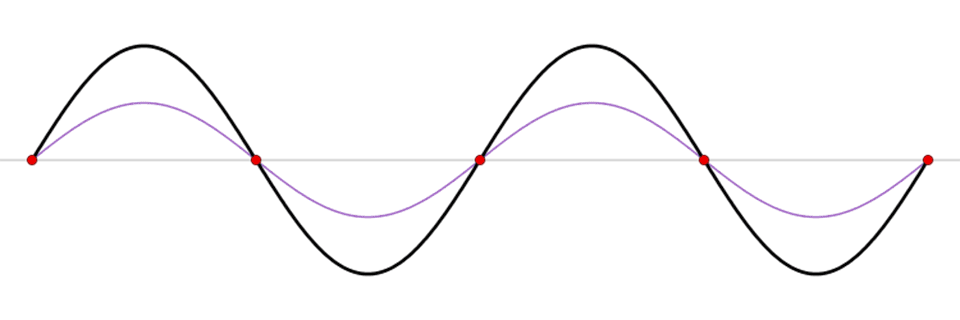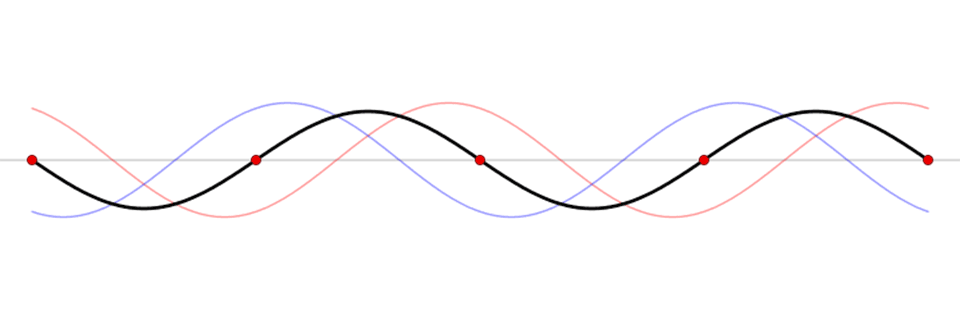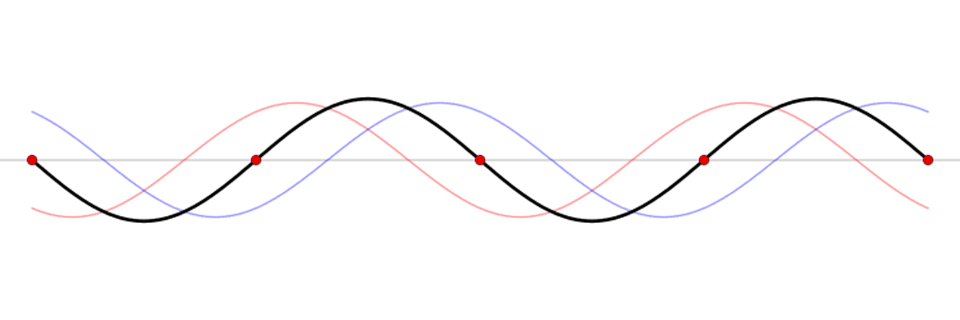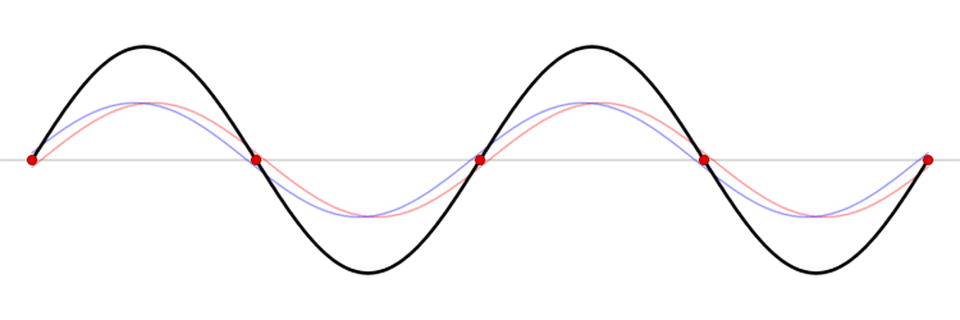
This animation reveals a standing wave (black) depicted as a sum of two propagating waves touring in reverse instructions (blue and pink). Related in movement to a seesaw, a seiche is a standing wave by which the most important vertical oscillations are at every finish of a physique of water with very small oscillations on the “node,” or heart level, of the wave. Standing waves can kind in any enclosed or semi-enclosed physique of water, from an enormous lake to a small espresso cup.
Seiches and meteotsunamis. What is the distinction?
Seiches and meteotsunamis are sometimes grouped collectively, however they’re two completely different occasions. Winds and atmospheric stress can contribute to the formation of each seiches and meteotsunamis; nonetheless, winds are sometimes extra essential to a seiche movement, whereas stress typically performs a considerable position in meteotsunami formation. Generally a seiche and a meteotsunami may even happen on the identical time. Seiches are standing waves with longer intervals of water-level oscillations (sometimes exceeding intervals of three or extra hours), whereas meteotsunamis are progressive waves restricted to the tsunami frequency band of wave intervals (two minutes to 2 hours). Seiches are often restricted to partially or totally enclosed basins, akin to Lake Erie. Meteotsunamis can happen in such basins however are additionally prevalent on the open coast. A single meteotsunami can journey lengthy distances and affect a really massive vary of the shoreline.
You probably have noticed water sloshing forwards and backwards in a swimming pool, bathtub, or cup of water, you might have witnessed a small-scale seiche (pronounced saysh). On a a lot grander scale, the identical phenomenon happens in massive our bodies of water akin to bays and lakes. A seiche could happen in any semi- or fully-enclosed physique of water.
Seiches are sometimes brought on when robust winds and speedy modifications in atmospheric stress push water from one finish of a physique of water to the opposite. When the wind stops, the water rebounds to the opposite facet of the enclosed space. The water then continues to oscillate forwards and backwards for hours and even days. In a similar way, earthquakes, tsunamis, or extreme storm fronts can also trigger seiches alongside ocean cabinets and ocean harbors.
Lake Erie is understood for seiches, particularly when robust winds blow from southwest to northeast. In 1844, a 22-foot seiche breached a 14-foot-high sea wall killing 78 folks and damming the ice to the extent that Niagara Falls quickly stopped flowing. As just lately as 2008, robust winds created waves 12 to 16 toes excessive in Lake Erie, resulting in flooding close to Buffalo, New York. Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana, can also be recognized to routinely kind small seiches after the passage of afternoon squall strains throughout summer time months.
In among the Nice Lakes and different massive our bodies of water, the time interval between the “excessive” and “low” of a seiche might be as a lot as 4 to seven hours. That is similar to the time interval between a excessive and low tide within the oceans, and is commonly mistaken as a tide.